Lesson 1 – Understanding lung cancer
← Back to LessonsWHAT IS LUNG CANCER?
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in one or both lungs. These abnormal cells do not develop into healthy lung tissue; instead, they divide rapidly and form tumors. As tumors grow, they can interfere with the lungs' ability to supply oxygen to the bloodstream.
THE 2 PRIMARY TYPES OF LUNG CANCER
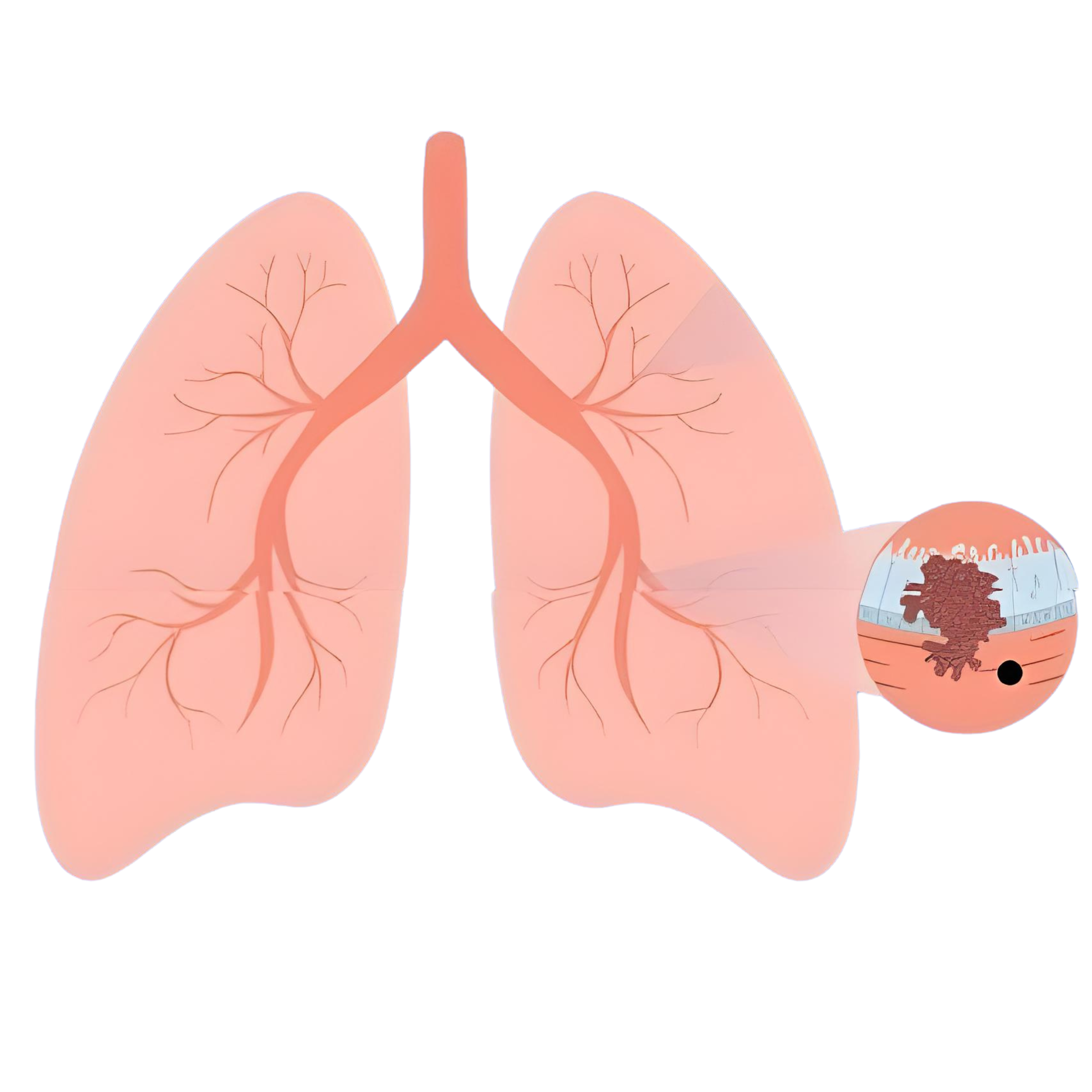
1. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): This is the most common form, accounting for about 85% of all cases.
NSCLC includes several subtypes, such as:
- Adenocarcinoma: Often found in people who have smoked but is also the most common type among non-smokers. Typically forms in the outer areas of the lungs.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Linked to smoking, forms in the central part of the lungs near a bronchus.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: Can appear in any part of the lung and tends to grow and spread quickly.
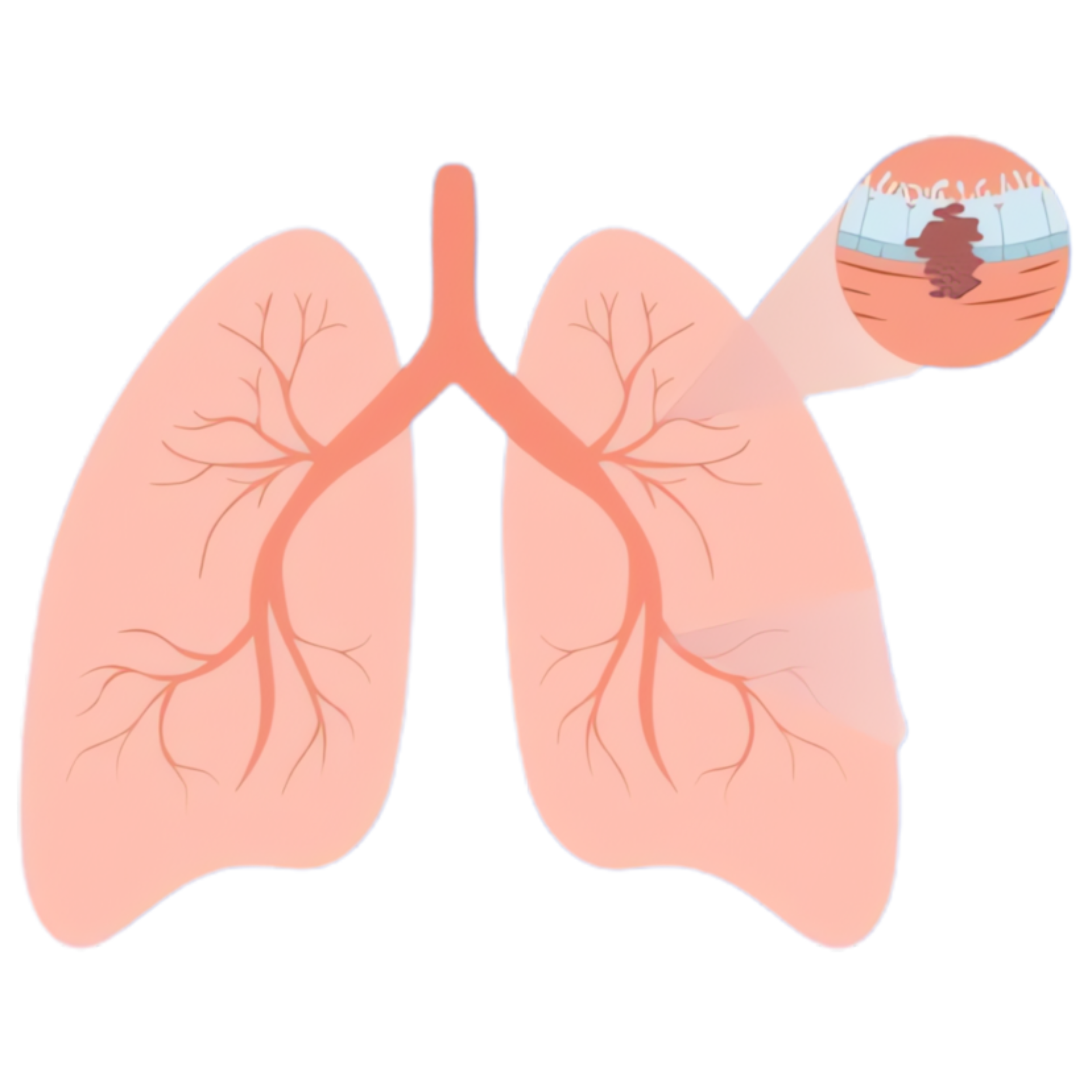
2. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): This type is less common but more aggressive. It is strongly associated with cigarette smoking. SCLC grows quickly and often spreads to other parts of the body early in the disease.